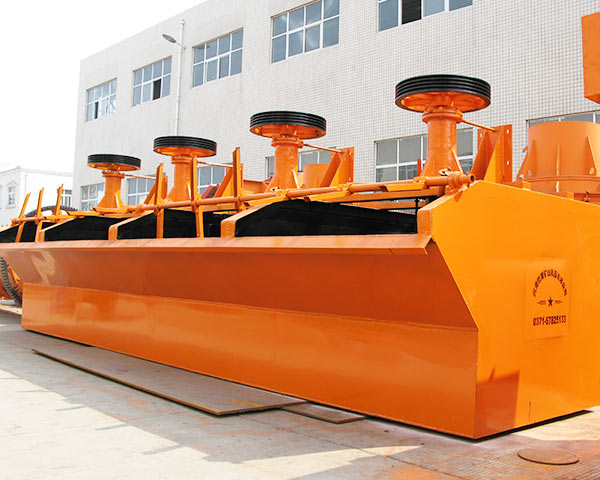
The Handling Materials and Description of Froth Flotation:
Froth Flotation is widely used for roughing, concentrating and recovering flotation of nonferrous metals that include copper, lead, zinc, nickel and molybdenum, ferrous metal, It can also be used for separating nonmetallic minerals. like coal and fluorite.
.jpg)
The Advantages and Benefits of Froth Flotation:
1. Large inhaling capacity and low energy consumption.
2. Process is easy to be changed.
3. Reasonable circulation of pulp decreases coarse sand sedimentation.
.jpg)
The Working Process of Froth Flotation:
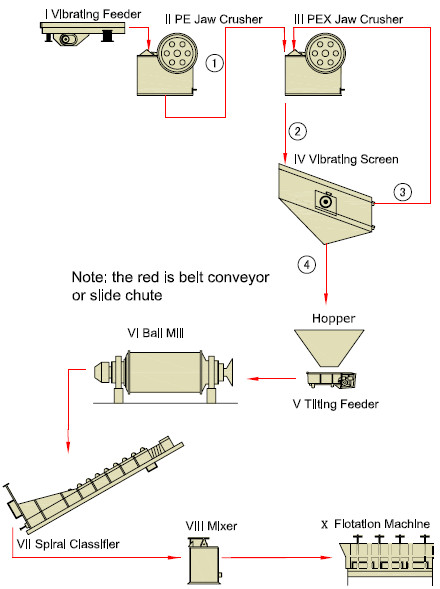
The impellers are driven through V-belt transmission, which brings centrifugal effect to form the negative pressure. On the one hand, the froth flotation machine inhales sufficient air to mix with ore slurry; on the other hand it stirs ore slurry and mix with medication to form the mineralized froth. To adjust the height of flashboard to control the liquid level and make the useful froth scraped by loam board.
Before starting the machine, first check the bolts of all spare parts and before stopping the machine, manually spin the wheel to prevent the depositing of sediment from increasing the load of electro motor. During the working process, carefully adjust the height of the flashboard to maintain the stability of the liquid level, so that the mineralized bubbles on the liquid surface of the pump can be timely scraped to the launder. A certain space should be maintained between the impeller and the stator, and when the impeller is abraded, it should be changed timely, and the bearing inside the pump should be maintained every three month.
Mix the mashed rocks with water and necessary reagent in the mixing chute, and inject them to the pulp chute. Lead air to the pulp to make it form large quantities of bubbles, and some mineral particles that are difficult to get moist in water and that are generally called hydrophobic mineral particles will stick on the bubbles and float with the bubbles to the surface of the pulp to form mineralized bubble layer, and some other mineral particles that are easy to get moist in water and that are called hydrophilic mineral particles do not stick on the bubbles but stay in the pulp to discharge the mineralized bubbles containing specific minerals, thus completing the separation process.
Technical data
Quick Way To Get Price
Note:For product inquiry or order requirements, Please fill the following form,
and we will contact you within one business day,
and all your information is kept confidential and is not shared with any third parties.

 30 seconds for connecting customer service
30 seconds for connecting customer service
 30 minutes for getting technical answer
30 minutes for getting technical answer
 24 hours for getting free solution plan
24 hours for getting free solution plan


.jpg)
.jpg)
